General relativity treats space and time on the same footing, that is not what is done in Hamiltonian formulations. Therefore, in order to discuss general relativity in a Hamiltonian fashion, one needs to break that equal footing. This requires a space-time splitting, since only time derivatives are transformed to momenta but not space derivatives.. The Arnowitt-Deser-Misner ( ADM) formalism (named for its authors Richard Arnowitt, Stanley Deser and Charles W. Misner) is a Hamiltonian formulation of general relativity that plays an important role in canonical quantum gravity and numerical relativity. It was first published in 1959.
PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint

(PDF) The Hamiltonian of Einstein affinemetric formulation of General

Hamiltonian analysis of the BFCG formulation of general relativity

(PDF) General Relativity on a Null Surface Hamiltonian Formulation in
PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint

PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint

Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity M O Katanaev

(PDF) Change in Hamiltonian General Relativity with Spinors

(PDF) The Hamiltonian formulation of General Relativity myths and

(PDF) Role of surface integrals in the hamiltonian formulation of

(PDF) Hyperbolic Hamiltonian equations for general relativity
Figure 1 from Hamiltonian Analysis In New General Relativity Semantic

PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint

(PDF) The Principle of Covariance and the Hamiltonian Formulation of

(PDF) REFORMULATION OF LAGRANGIAN & HAMILTONIAN IN THEORY OF RELATIVITY

Hamiltonian formulation of General Relativity and applications LF
PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint
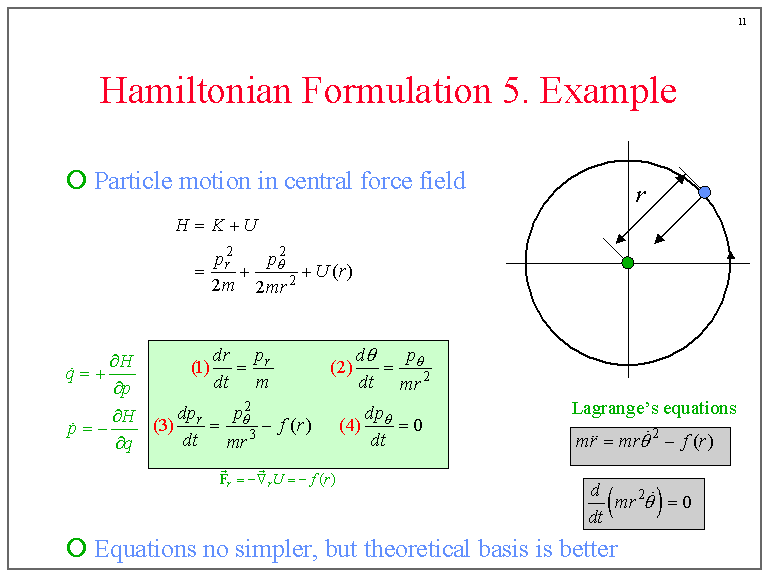
Hamiltonian Formulation 5. Example

(PDF) New Hamiltonian Formulation of general relativity
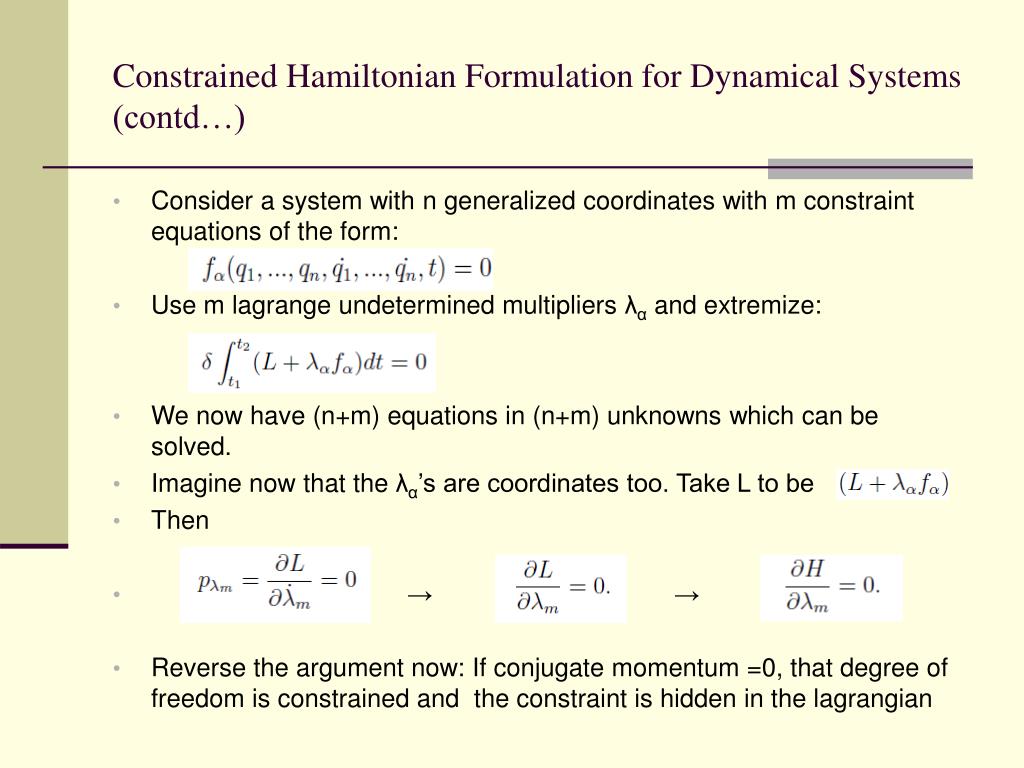
PPT Hamiltonian Formulation of General Relativity PowerPoint
Hamiltonian formalisms provide powerful tools for the computation of approximate analytic solutions of the Einstein field equations. The post-Newtonian computations of the explicit analytic dynamics and motion of compact binaries are discussed within the most often applied Arnowitt-Deser-Misner formalism. The obtention of autonomous Hamiltonians is achieved by the transition to Routhians.. In this chapter we provide a self-contained exposition of the classical Hamiltonian formulation of General Relativity. It is mandatory to know all the details of this classical work as it lays the ground for the interpretation of the theory, the understanding of the problem of time and its implication for the interpretation of quantum mechanics, the meaning of observables, the relation between.